This paper aims to enhance the moral and vocational qualities of college students by integrating moral education elements into career planning education. The BOPPPS teaching model is constructed, comprising six modules: introduction, objectives, pre-test, participatory learning, post-test, and summary, to effectively stimulate students’ interest and initiative. Moral education elements are integrated into career planning education through an intelligent teaching platform, incorporation into teaching processes, and the use of the second classroom to promote in-class and out-of-class linkages. Additionally, a fuzzy classroom teaching evaluation system is developed to assess the effectiveness of career planning education. The results indicate high reliability and validity of the evaluation system, with an alpha coefficient exceeding 0.8, a KMO value of 0.938, and a Bartlett’s test P-value of 0.000. Students’ positive classroom mood improved significantly from 35.79% to 68.42%, alongside an enhanced evaluation of classroom learning. The findings demonstrate the practical value of this approach in advancing education reform.
As the education reform is more and more emphasized by the relevant departments, the number of college students is rising every year, and the career planning education can help the recipients of education to determine the future development path and life goals, and also enhance the students’ moral qualities, values and sense of social responsibility through moral education [20,18]. Therefore, bringing moral education elements into students’ career planning education has obvious significance of education reform, in the comprehensive cultivation of college students, improve college students’ professional skills and knowledge level, at the same time, cultivate college students’ moral quality and sense of social responsibility, promote college students’ rapid integration into the work environment and the social environment after graduation, and highlight the effect of college students’ career planning education [4,2]. Moral education elements into the development of life stages, to improve the comprehensiveness of career planning, and to promote college students in the development of personal life stages in the process of personal interests as a prerequisite, give full consideration to the social welfare and national development, and improve the patriotic sentiment of the students. Moral education can also promote college students in the face of future pressure, can still set up the correct three views, improve the psychological ability to face the challenges of the future career to maintain positivity [17,11].
The root of education reform is to change the way of teaching students, so many scholars in the field of education have begun to study life stage development education and the integration of moral education elements. Literature [7] and others believe that the integration of moral education elements and brought into the college students’ career planning program can effectively improve the college students’ work ethic and sense of social responsibility. Literature [14] and others showed in their research that the use of case studies and group discussions in the career planning courses for college students can better guide students to think deeply about the relationship between ethics and career development. Literature [1] and others take the professional characteristics of college students as the basis, bring the moral education element into the career planning education, look for the corresponding unit as a case study, analyze the character and skill requirements of the employees in this kind of unit, so as to improve the college students’ professional ethics and innovative spirit. Literature [15] and others believe that often organizing education recipients to contact volunteer services, in-depth training institutions or enterprises can enhance students’ knowledge of society, understand the social industry demand for graduating college students, and improve the ability of college students in all aspects of social practice. Literature [9] points out that organizing students to visit enterprises or do internships frequently can promote students’ understanding of the needs and requirements of various industries and occupations, and provide them with more in-depth insights. Literature [16] discusses in its study that in the process of organizing students’ vocational experience in enterprises, a student mentor is appointed in the enterprise, through which the mentor completes the vocational guidance and moral education of college students, so as to change the existing vocational outlook of the recipients of education in a positive direction. Literature [10] and others believe that in order to improve the three views of education recipients from the positive direction and enhance the quality of moral education, first of all, we need to strengthen the construction of the teaching staff. Moral education training for teachers of career planning education, to change the existing knowledge of the teaching team’s mode of instruction, under the guidance of the teacher’s words and deeds, to promote the development of the correct values of the students.
Due to the optimization and adjustment of industrial structure, there is a mismatch between the employment demand of college students and the job demand of enterprises, such as the phenomenon of joblessness, slow employment and slow employment. In the face of changes in college students’ outlook on employment, career choice and employment psychology, it has become more and more important to do a good job in the classroom of life-stage development of education recipients. As an important part of helping college students to clarify career goals, make reasonable plans, cultivate vocational literacy, and improve comprehensive ability, the career planning course for college students has a pivotal effect on guaranteeing that education recipients can find ideal jobs. Bringing the BOPPPS teaching model into the career planning classroom, through the introduction, objectives, pre-test, participatory learning, post-test, and summary of the model, we start from attracting the interest of college students in learning, informing them of the teaching objectives before teaching in order to realize the goal orientation, and conducting a pre-study mapping test for students to understand the relevant learning conditions of the students, and then designing interactive and participatory teaching activities based on the results of the test to increase the practical activities of the course. Based on the results of this test, interactive and participatory teaching activities are designed to increase the practical activities of the course and effectively arouse students’ interest and initiative. The paths of educational reform and innovative strategies for the life-stage development of education recipients are analyzed, providing targeted guidance to ensure that recipients of higher education are fully employed after exposure to the changed mode of knowledge delivery.
The original BOPPPS instructional model, obtained from the basic training of knowledge givers in a particular country, is a goal-oriented, student-centered delivery method. Designing the whole teaching process into six modules: introduction, objectives, pre-test, participatory learning, post-test, and summary, the BOPPPS teaching model is summarized as shown in Table 1, and the initial letters of the six modules constitute the BOPPPS delivery method. The model starts from attracting the interest of college students in learning, informs the teaching objectives before teaching to realize goal orientation, and conducts a pre-test for students to understand the relevant learning conditions of students, and then designs interactive and participatory teaching activities based on the results of this test to increase the practical activities of the course and effectively arouse the interest and initiative of students [19]. After the completion of the teaching activities, the knowledge mastery status is realized by issuing a paper, and finally, a teaching summary is conducted, and this summary is used as an introduction to the next chapter.
| Name | Main tasks | Pedagogical elements of the curriculum |
| Import |
Improvement of traditional methods to increase the concentration of the education
recipient and to strengthen the perception of knowledge by the education recipient |
Why |
| Target |
Developing the content of knowledge lectures so that the recipients
understand what they can do with the knowledge. |
Who/Do What/Under What/How well |
| Front Side |
Issuing a paper to the recipients of education, analyzing the basis of the information
received by the recipients of education and preparing them for future teaching. |
Know What |
| Participatory Learning |
The main part of classroom teaching, involving
students in classroom activities and active learning |
Whether or not |
| Back side |
Testing the effectiveness of the stages of developing
knowledge delivery and mastering the learning outcomes |
How well |
| Summarize | Summarize the lesson, reflect on what you have learned and lead to the next lesson | – |
College students’ career planning course is an inevitable requirement for guiding knowledge receivers to establish learning objectives during college, clarify their own career development direction, purposefully construct knowledge, ability and quality structure during college study, and realize the reasonable matching of people and jobs. It helps students to plan for the future and effectively promotes students’ employment. College students career planning course has been used in the lecture-style teaching, the lack of fun and interactivity, while the BOPPPS teaching model to make the teaching design more systematic, so that the degree of student participation, so that students can directly experience the knowledge and skills in the classroom, the classroom practice to enhance, conducive to the change of the current inherent method of instruction. Therefore, based on the teaching status quo of college students’ career planning course, in order to change the teaching knowledge delivery model and enhance the nurturing effect of the course, the constructed course adopts the model of integrating the BOPPPS delivery method with the moral education elements to carry out teaching [6].
BOPPPS model and moral education elements fusion teaching mode, flipped classroom can play the effect of optimizing the BOPPPS model. In the course session, the flipped classroom allows students to learn what they have learned in this class through online videos before class, explore and practice in class according to the BOPPPS teaching model, and allow students to digest and absorb the knowledge through homework after class. Effectively demonstrate the use of the classroom model of integrating BOPPPS and moral education elements in the course of life-stage development of education recipients, take the chapter of self-knowledge in the course as an example to do the instructional design, and the instructional design of self-knowledge based on the BOPPPS model is shown in Table 2. In participatory learning, Hollander’s theory pre-test is issued, and students explain the career interests they have mastered and explore their own career interests. Eventually, they analyze each other according to the theory of career interest and digest and absorb the knowledge from the class.
| Learning before class | Teaching and Learning Program | Teaching Activities | Student Activities |
| Learning during the lesson | Introduction | One week before the class, the teacher releases a video about Hollander’s theory of vocational interest in Learning Channel and reminds students to study through the related Ranjian. | Actively participate and share what they have written to reinforce student self-awareness. |
| Objectives | 1. Ask students to write 10 sentences “I am a person”. 2. Teacher puts forward the concept of self-knowledge to introduce the content of this chapter. 3. | Reflections | |
| Pre-test | Test students’ knowledge, ability, and attitude goals. | Completion of pre-test | |
| Participatory Learning | Take the Hollander’s Theory pre-test. | Students explain the career interests they have mastered and explore their own career interests | |
| Post-test | Showing students’ study notes on vocational interest theory, supplementing and answering students’ explanations, and organizing students to participate in vocational interest exploration to understand their own vocational interests and vocational personalities. | Study Pass Completion Posttest | |
| Summarize | Orally summarize and repeat the teaching key points: the concepts of interest and vocational interest, the way of vocational interest exploration. | Digest, Understand | |
| Learning after school | – | Assign homework: students analyze each other what kind of person each other is in their own eyes, and what kind of jobs they are suitable for | Students analyze each other’s knowledge based on theories of career interests and digest and absorb what they have learned in class. |
In the moral education elements of integration of education continues to develop today, network resources can not be ignored, the birth of the moral education cloud classroom, so that the education work to see the value of the Internet + where the new media era, had to start thinking about the cloud classroom, wisdom classroom this type of network resources teaching, moral education has what kind of role in promoting. Then, the use of the Internet platform to build a wisdom moral education teaching platform will enable teachers to classify, summarize and integrate the excavated elements of moral education on the basis of skilled use of network technology, and gather them in the platform in the form of videos, movies, etc. At the same time, they can introduce typical events around them and hot cases on the Internet into their teaching content, so that students can have a higher moral literacy and sense of social responsibility, and improve their health literacy in a comprehensive way. College students’ health literacy to lay a theoretical foundation.
As one of the compulsory courses for college students, the career planning class is an important way to make students understand the direction of social development, the direction of employment demand and the needs of a variety of careers, and it is also an important form of improving the level of college students’ health literacy in practice. The integration of moral education elements in college students’ career planning requires the integration of cultural elements such as value norms, business concepts, and development goals with those of enterprises in planning teaching, so that students can understand the employment requirements of modern enterprises. Gradually infiltrate the vocational norms, vocational behavior, vocational mission and vocational sense of honor into students’ cognition, and cultivate high-quality talents with ideals, morals, knowledge and vocational skills that are truly suitable for the needs of modern enterprises.
School culture requires teachers and students to love school and make school their home. Enterprise culture requires employees to take the enterprise as home, love and dedication. Love of work, love of school, in its essence, is a kind of attachment to the environment in which people are located, the expression of love. Focusing on the teaching objectives of moral education, carrying out the moral education practice activities of college students’ career planning with elements of enterprise culture and vocational elements is a powerful way to improve the effect of moral education teaching. Figure 1 shows the integration path of moral education elements in the career planning courses in colleges and universities, such as hiring enterprise masters and skill experts to come to school regularly to give special lectures and skill demonstration observation classes, etc., to knot their successful experience, so that students can accept the inculcation of the excellent enterprise culture, and correctly recognize the importance of their own career growth planning [8].

In fuzzy theory, fuzzy sets are the main tool for describing phenomena and the theoretical basis for establishing a fuzzy assessment system. The main difference between a fuzzy set and an ordinary set is that the latter is represented by the characteristic function, while the former is represented by the affiliation function. If the characteristic function takes only 0 and 1 and is generalized to the interval [0,1], the affiliation function of the fuzzy set can be given as: \[\label{GrindEQ__1_} X_{A} (x)=a,0\le a\le 1 , \tag{1}\]
Where \(A\) is a fuzzy set on the domain \(X=\left\{x_{1} ,x_{2} ,\cdots ,x_{n} \right\}\) and \(X_{A} {}^{{'} } (x)\in [0,1]\) is the degree of affiliation of \(X\) to \(A\), where \(x\in X\) using the Eq. (1) can clearly portray the affiliation of the object under study to the set. In addition, when \(X_{A} (x)\) takes 1 it indicates that the degree of affiliation is 1, i.e., it is said that \(X\) belongs to \(A\), while when \(X_{A} (x)=0\), it indicates that \(X\) does not belong to \(A\) If any value bounded between [0,1] is taken, it indicates the degree to which \(X\) belongs to \(A\). It can be seen that the affiliation function is a generalized eigenfunction, and the eigenfunction is a special case of the affiliation function. A fuzzy set, on the other hand, is uniquely determined by its affiliation function \(X_{A} (x)\). In other words, the key to determining a fuzzy set is the degree of affiliation of each element in a given set, which can be measured by a real number in the closed interval [0,1].
In general, ambiguity refers to the fact that the concept is vague, i.e., there is no clear criterion for judgment, or that there is an equal and opposite phenomenon between the differences of objective things. Or whether an element belongs to a given set cannot be answered simply by a yes or no answer. Instead, it can only be portrayed in terms of the degree of belonging, and the description of the magnitude of this degree can be expressed in terms of an affiliation function [13]. There are two representations of a fuzzy set in a finite field, one of them is the vector representation, let \(A\) be a fuzzy subset on a finite field \(X=\left\{x_{1} ,x_{2} ,\cdots ,x_{n} \right\}\), if the affiliation function of \(A\) is \(X_{A} (x)\), then the vector representation of \(A\) is \(A=\left\{X_{A} \left(x_{1} \right),X_{A} \left(x_{2} \right),\cdots ,X_{A\left(x_{n} \right)} \right\}\).
The second is the Zadeh representation, let \(A\) be a fuzzy subset on a finite field \(X=\left\{x_{1} ,x_{2} ,\cdots ,x_{n} \right\}\), and if the degree of affiliation of \(x_{i}\) to \(A\) is \(X_{A} \left(x_{i} \right)\), then the Zadeh representation of \(A\) is. \[\label{GrindEQ__2_} A=\frac{X_{A} \left(x_{1} \right)}{x_{1} } +\frac{X_{A} \left(x_{2} \right)}{x_{2} } +\ldots +\frac{X_{A} \left(x_{n} \right)}{x_{n} } . \tag{2}\]
Also noted as: \[\label{GrindEQ__3_} A=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\frac{X_{A} \left(x_{i} \right)}{x_{i} } {\rm \; } {\rm or\; }A=\bigcup _{i=1}^{n}\frac{X_{A} \left(x_{i} \right)}{x_{i} } . \tag{3}\]
In the Zadeh representation, \(\frac{X_{A} \left(X_{i} \right)}{X_{i} }\) does not represent a fraction and + does not represent a summation. The denominator is the element \(x_{i}\) in the domain \(X\), and the numerator is the degree of affiliation corresponding to \(x_{i}\), i.e., \(x_{i}\) seeks the degree of belonging to \(A\). Fractional equation \(\frac{X_{A} \left(x_{i} \right)}{x_{i} }\) represents the correspondence between element \(x_{i}\) and its degree of affiliation to \(A\), and terms with degree of affiliation 0 may be left out.
Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation is built on the basis of fuzzy set, which is a kind of evaluation model with excellent and feasible nature that is widely used in educational assessment at present. To make a comprehensive evaluation of college students’ career planning teaching design affected by multiple moral education elements, its biggest feature is that it integrates the information of all the intrinsic elements in the process of quantifying the career planning teaching design, and the loss of information is very small, so the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation has a wide range of practical value not only for the evaluation of teaching design, but also in all other kinds of evaluation fields [12]. In the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model, let the set of indicators of moral education elements for \(U=\left\{U_{1} ,U_{2} ,\cdots ,U_{n} \right\}\), the set of rubrics for \(V=\left\{V_{1} ,V_{2} ,\cdots ,V_{m} \right\}\), the fuzzy subset of indicator weight coefficients for \(\left. W=\left\{w_{1} \right. ,w_{2} ,\cdots ,w_{n} \right\}\), \(U\) of the \(i\)th indicator for the corresponding rubrics in the set of V in the evaluation of the \(V_{1} ,V_{2} ,\cdots ,V_{m}\) degree of affiliation for \(r_{1} ,r_{2} ,\cdots ,r_{i}\), respectively, so that the \(U\) of this indicator \(U_{i}\) for the degree of affiliation for each of the evaluations of \(V\) composed of a fuzzy subset of the \(V\) on the notation of \(R_{i} =\left\{r_{1} ,r_{2} ,\cdots ,r_{in} \right\}\). for each of the indicators \(U_{i} (I=1,2,\cdots ,n)\) to find out the corresponding \(R_{i}\), put together, the constitute a fuzzy matrix on \(U\times V\), i.e.: \[\label{GrindEQ__4_} R=\left(\begin{array}{c} {R_{1} } \\ {R_{2} } \\ {\vdots } \\ {R_{n} } \end{array}\right)=\left(\begin{array}{cccc} {r_{11} } & {r_{12} } & {\cdots } & {r_{1m} } \\ {r_{21} } & {r_{22} } & {\cdots } & {r_{2m} } \\ {\vdots } & {\vdots } & {} & {\vdots } \\ {r_{n1} } & {r_{n2} } & {\cdots } & {r_{nm} } \end{array}\right). \tag{4}\]
Fuzzy matrix multiplication of matrices \(W\) and \(R\) yields: \[\label{GrindEQ__5_} B=W\cdot R=\left[\begin{array}{lll} {w_{1} } & {w_{2} \cdots } & {w_{n} } \end{array}\right]\cdot \left(\begin{array}{cccc} {r_{11} } & {r_{2} } & {\cdots } & {r_{1m} } \\ {r_{21} } & {r_{22} } & {\cdots } & {r_{2m} } \\ {\vdots } & {\vdots } & {} & {\vdots } \\ {r_{n1} } & {r_{n2} } & {\cdots } & {r_{nm} } \end{array}\right)=\left[\begin{array}{ll} {b_{1} \; b_{2} \cdots } & {b_{m} } \end{array}\right]. \tag{5}\]
Among them: \[\label{GrindEQ__6_} b_{j} =V_{i=1}^{n} \left(w_{i} \wedge r_{ij} \right)=\left(w_{1} \wedge r_{1_{j} } \right)V\left(w_{2} \wedge r_{j_{j} } \right)\vee \ldots \vee \left(w_{n} \wedge r_{n_{j} } \right),(j=1,2,\cdots ,m) . \tag{6}\]
Normalization of B is obtained: \[\label{GrindEQ__7_} B^{*} =\left(b_{1}^{*} ,b_{2}^{*} ,\cdots ,b_{m}^{*} \right) . \tag{7}\]
Among them: \[\label{GrindEQ__8_} b_{j}^{*} =\frac{b_{j} }{b_{1} +b_{2} +\ldots +b_{n} } ,(j=1,2,\cdots ,m) . \tag{8}\]
Finally, the evaluation results of the college student career planning course design that incorporates elements of moral education are synthesized and evaluated step by step toward higher-level indicators until the highest level. The comprehensive evaluation model thus established is called the multilevel, or multilevel, fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model. Because the operation takes into account various factors affecting the evaluation results, its quantitative results can better reflect the actual situation of integrating moral education elements into the teaching of college students’ career planning [5,3].
This study combines the characteristics of tourism service and management majors in colleges and universities, according to the colleges and universities to bring moral education elements into the career planning course, to prepare a questionnaire on the status of the teaching of career planning courses in tourism service and management majors for college students. This study selected 1-4 grade tourism service and management majors in Jiangsu Province colleges and universities as the research object, through the questionnaire star to the students were issued a total of 330 electronic questionnaires, excluding 6 questionnaires with the same consecutive answers, and recovered 324 valid questionnaires, the effective questionnaire recovery rate of 98.2%.
The questionnaire of this study mainly investigates the problems of teaching career planning courses for tourism service and management majors in colleges and universities, which contains three dimensions of classroom learning emotions, classroom learning input, classroom learning evaluation, a total of 14 questions, and the questionnaire adopts the Likert 5-point method of scoring. In this questionnaire, 1 point is counted for very non-conformity, 2 points for non-conformity, 3 points for general conformity, 4 points for comparative conformity, and 5 points for very conformity.
In this study, Cronbacha coefficient was used as an index to determine the reliability. SPSS27.0 was used to analyze the reliability of the data to obtain the reliability of each scale, and the questionnaire reliability, KMO and Bartlett check are shown in Table 3. The alpha coefficient of each dimension of the questionnaire is greater than 0.8, which indicates that the overall level of reliability is high, and in the output of SPSS27.0, the value of KMO is 0.938, which is greater than 0.7. At the same time, the p-value corresponding to Bartlett’s test of sphericity is 0.000, which indicates that it is suitable to do factor analysis of the data.
| Scale | Subject | \(\alpha\)-coefficient |
| Classroom Learning Mood | 4 | 0.897 |
| Classroom Engagement | 5 | 0.912 |
| Classroom Learning Assessment | 5 | 0.893 |
| General Questionnaire | 14 | 0.934 |
| KMO Sample Suitability Quantity | .938 | |
| KMO Sample Suitability Quantity | Approximate chi-square | 5478.517 |
| df | 325 | |
| Sig. | .000 | |
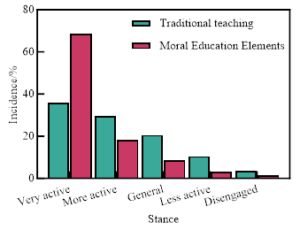
Classroom learning emotion refers to an attitude and experience formed by students in the process of classroom learning as to whether the content, process and outcome of learning are consistent with their own needs, and an emotional response formed in the process of communication with the teacher. By comparing the original career planning teaching and the integration of moral education elements into career planning teaching, the results of the survey were counted, and the teaching-learning-emotional comparison is shown in Figure 2. It can be seen that the traditional career planning teaching method, students in the classroom learning mood is not good, for the classroom content is very positive, very interested in the students only reached 35.79%, more positive and more interested in the students of 29.43%, the classroom career planning to tell the content of the students are not interested in 14.22%. However, after integrating the moral education element into the teaching of career planning, the teacher brings in a lot of classic cases in the classroom, and often organizes students to go deep into the enterprise for understanding and internship, which greatly increases the interest of students, so the students who are very active and very interested in the classroom reach 68.42%, the students who are more active and more interested in the classroom reach 18.33%, and the students who are not interested in the classroom drop to 4.72%. It can be seen that the integration of moral education elements into the teaching of career planning has obviously increased students’ enthusiasm for career planning classroom teaching and mobilized students’ learning mood in the classroom.
Classroom learning assessment refers to the comprehensive assessment activities of measuring, analyzing and evaluating the learning process and learning effects of students in accordance with the relevant assessment standards, guided by the learning objectives. According to the different spaces where teaching activities take place, learning assessment can be divided into in-class and out-of-class assessment. Learning assessment outside the classroom refers to the evaluation of students’ learning effect in a certain period of time or at the end of a semester, which is more inclined to summative evaluation. In-class learning evaluation refers to the formative evaluation of students’ learning status, learning performance and learning process in the classroom, and Table 4 shows the comparison of teaching learning evaluation. By evaluating the traditional career planning teaching as well as the classroom learning of career planning teaching after the integration of moral education elements into the career planning course, the integration of moral education elements into the career planning course can effectively improve students’ evaluation of classroom learning. By integrating moral education elements into the career planning course, students’ highest evaluation of the course increased from 19.4% to 59.3%, teachers’ highest evaluation of students’ performance increased from 20.4% to 61.6%, students’ highest evaluation of the results of vocational activities increased from 21.0% to 60.4%, the highest evaluation of receiving teachers’ praises increased from 21.6% to 60.9%, and the highest evaluation of the learning outcomes increased from 19.8% to 59.4%. Therefore, integrating moral education elements into the career planning course is an important way to improve the evaluation of students’ learning in the classroom.
| Title | Very inconsistent | It doesn’t fit. | Fair | Quite compliant | Very compliant | |||||
| A1 | A2 | A1 | A2 | A1 | A2 | A1 | A2 | A1 | A2 | |
| Student Evaluation of the Course | 4.3 | 1.1 | 27.2 | 4.1 | 21 | 18.4 | 28.1 | 17.1 | 19.4 | 59.3 |
| Teacher evaluation of student performance | 6.1 | 1.2 | 27.5 | 2.6 | 20.7 | 17.2 | 25.3 | 17.4 | 20.4 | 61.6 |
| Evaluation of the results of vocational activities | 5.8 | 1.3 | 23.5 | 3.7 | 22.5 | 16.3 | 27.2 | 18.3 | 21 | 60.4 |
| Evaluation of praise received from teachers | 4.7 | 1.2 | 26.5 | 2.1 | 24.7 | 18.1 | 22.5 | 18.7 | 21.6 | 60.9 |
| Evaluation of learning outcomes | 5.6 | 0.7 | 25.6 | 2.1 | 23.1 | 17.2 | 25.9 | 20.6 | 19.8 | 59.4 |
In the questionnaire designed for students in this study, a score of 1 was given for very non-compliant, 2 for non-compliant, 3 for average, 4 for relatively compliant and 5 for very compliant. Using the mean value of 3 as a boundary, a score of 4 or 5 indicates that the teaching of career planning courses is good, and a score below 3 indicates that the teaching of career planning courses is poor. According to the basic conditions of normal distribution, in order to judge whether the sample obeys normal distribution, it is necessary to judge whether the absolute value of kurtosis is less than 10, and whether the absolute value of skewness is less than 3. The dimensions of the teaching of career planning courses are shown in Table 5, and each variable basically obeys normal distribution. On the whole, if the mean value of each dimension is greater than 5, the teaching situation of career planning course for tourism service and management majors in school high schools is ideal.
| Dimensionality | N | Mean | Standard deviation | Skewness | Kurtosis | ||
| Statistics | Statistics | Statistics | Statistics | Error | Statistics | Error | |
| Classroom Learning Emotions | 324 | 5.31 | 1.09 | -0.188 | .135 | -1.100 | .270 |
| Classroom Learning Engagement | 324 | 5.33 | 1.08 | -0.028 | .135 | -1.301 | .270 |
| Classroom Learning Assessment | 324 | 5.45 | 1.01 | .035 | .135 | -.991 | .270 |
| Overall Teaching of Career Planning Courses | 324 | 5.35 | .766 | .540 | .135 | -1.235 | .270 |
Based on practical experience in teaching, it is proposed to change the teaching philosophy to create an effective classroom. For university teachers, increase teacher training and improve professional competence. Deepen the analysis of learning conditions to create individualized teaching. At the same time, increase the course hours, strengthen the knowledge penetration, but also reduce the class size and improve the quality of teaching. Through post-research summarization, continuous improvement of teaching and other work paths. The teaching mode based on the combination of BOPPPS lecture method and college students’ career planning classroom has scientific teaching design, standardized teaching process, participatory teaching method, which makes students change from passive receivers to active participants, and greatly improves the stage performance of the course’s lecture.
This paper proposes to combine the BOPPPS teaching model with the college students’ career planning classroom, and makes the teaching design to effectively promote the benign development of college education. In the analysis of the teaching effect of the career planning course, it was found that the alpha coefficient of each dimension of the questionnaire was greater than 0.8, the KMO value was 0.938, and the P-value of the Bartlett’s spherical test was 0.000, which showed that the overall level of reliability was high, and it was suitable for doing factor analysis on the data. Students’ positive mood in the classroom significantly increased from 35.79% to 68.42%, students’ highest evaluation of the course increased from 19.4% to 59.3%, and teachers’ highest evaluation of students’ performance increased from 20.4% to 61.6. The highest evaluation of students’ vocational activity results increased from 21.0% to 60.4%, the highest evaluation of receiving praise from teachers increased from 21.6% to 60.9%, and the highest evaluation of learning results increased from 19.8% to 59.4%. The research in this paper can effectively guide education recipients to establish correct worldview, life view and career values, guide students to integrate their personal pursuits and development with the needs of the country, make reasonable career decisions, and realize optimal personal development.