An outer independent double Roman dominating function (OIDRDF) on a graph \( G \) is a function \( f : V(G) \to \{0, 1, 2, 3\} \) having the property that (i) if \( f(v) = 0 \), then the vertex \( v \) must have at least two neighbors assigned 2 under \( f \) or one neighbor \( w \) with \( f(w) = 3 \), and if \( f(v) = 1 \), then the vertex \( v \) must have at least one neighbor \( w \) with \( f(w) \ge 2 \) and (ii) the subgraph induced by the vertices assigned 0 under \( f \) is edgeless. The weight of an OIDRDF is the sum of its function values over all vertices, and the outer independent double Roman domination number \( \gamma_{oidR}(G) \) is the minimum weight of an OIDRDF on \( G \). The \( \gamma_{oidR} \)-stability (\( \gamma^-_{oidR} \)-stability, \( \gamma^+_{oidR} \)-stability) of \( G \), denoted by \( {\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \) (\( {\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \), \( {\rm st}^+_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \)), is defined as the minimum size of a set of vertices whose removal changes (decreases, increases) the outer independent double Roman domination number. In this paper, we determine the exact values on the \( \gamma_{oidR} \)-stability of some special classes of graphs, and present some bounds on \( {\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \). In addition, for a tree \( T \) with maximum degree \( \Delta \), we show that \( {\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) = 1 \) and \( {\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) \le \Delta \), and characterize the trees that achieve the upper bound.
All graphs considered in this article are finite, undirected and simple. Let \(G=(V,E)\) be a graph of order \(|V(G)|=n\). For any vertex \(v\in V(G)\), the open neighborhood of \(v\) is the set \(N(v)=\{u\in V(G)\mid uv\in E(G)\}\) and the closed neighborhood of \(v\) is the set \(N[v]=N(v)\cup\{v\}\). We denote the degree of a vertex \(v\) in a graph \(G\) by \(\deg_{G}(v)\), or simply by \(\deg(v)\) if the graph \(G\) is clear from the context. Let \(\delta(G)\) and \(\Delta(G)\) denote the minimum and maximum degrees, respectively, of vertices in \(G\). We call a vertex of degree one a leaf, and its (unique) neighbor a support vertex. A support vertex is said to be strong if it has at least two leaf neighbors, otherwise is said to be weak.
A complete graph on \(n\) vertices is denoted by \(K_{n}\), while a complete bipartite graph with partite sets of size \(p\) and \(q\) is denoted by \(K_{p,q}\). We write \(P_{n}\) for the path of order \(n\), \(C_{n}\) for the cycle of order \(n\) and \(\overline{K_{n}}\) for the graph with \(n\) vertices and no edges. The distance \(d_{G}(u,v)\) between two vertices \(u\) and \(v\) in a connected graph \(G\) is the length of a shortest \((u,v)\)-path in \(G\) while the diameter, \(\mathrm{diam}(G),\) of \(G\) is the maximum distance among all pairs of vertices in \(G\). A tree is an acyclic connected graph. A star is the graph \(K_{1,m}\), where \(m\geq1\), the vertex of degree \(m\) is called the center of the star. A double star \(S_{r,s}\) is formed from two disjoint stars \(K_{1,r}\) and \(K_{1,s}\) by adding an edge joining their center vertices. A rooted tree \(T\) distinguishes one vertex \(r\) called the root.
Let \(k\geq1\) be an integer and let \(f\) be a function that assigns labels from the set \(\{0,1,\dots,k+1\}\) to the vertices of a graph \(G\). The active neighborhood \(AN(v)\) of a vertex \(v\in V(G)\) with respect to \(f\) is the set of all vertices \(w\in N(v)\) such that \(f(w)\geq1\). Let \(AN[v]=\{v\}\cup AN(v)\). A \([k]\)-Roman dominating function, abbreviated \([k]\)RDF, is a function \(f:V(G)\longrightarrow\{0,1,\dots,k+1\}\) satisfying the condition that for any vertex \(v\in V(G)\) with \(f(v)<k\), \({\sum\limits_{u\in N[v]}f(u)}\geq|AN(v)|+k\). The weight of a \([k]\)RDF is \(\omega(f)=\Sigma_{v\in V(G)}f(v)\), and the \([k]\)-Roman domination number \(\gamma_{\lbrack kR]}(G)\) of \(G\) is the minimum weight of a \([k]\)RDF on \(G\). A \(\gamma_{\lbrack kR]}(G)\)-function is a \([k]\)RDF of weight \(\gamma_{\lbrack kR]}(G).\) For a \([k]\)RDF \(f\) on \(G,\) let \(V_{i}^{f}=\{v\in V\mid f(v)=i\}\) for all \(i\in\{0,1,\dots,k+1\}.\) Consequently, any \([k]\)RDF \(f\) can be represented by \(f=(V_{0}^{f},V_{1}^{f},\dots,V_{k+1}^{f}),\) where the superscript \(f\) can be deleted in \(V_{i}^{f}\) when no confusion arises. The \([k]\)-Roman domination was introduced by Abdollahzadeh Ahangar et al. [1] and has been studied in [2,3]. Clearly, when \(k=1,\) \(\gamma_{\lbrack1R]}(G)\) matches with the usual Roman domination number \(\gamma_{R}(G)\) which has been surveyed and detailed in two book chapters and survey papers [4-8]. Moreover, if \(k=2\), then we deal with double Roman domination introduced by Beeler et al. [9], while if \(k=3,\) then we deal with triple Roman domination investigated in [1,10,11].
An outer independent \([k]\)-Roman dominating function abbreviated OI\([k]\)RDF, defined as an \([k]\)RDF \(f\) such that \(V_{0}^{f}\) is an independent set. The minimum weight of an OI\([k]\)RDF of \(G\) is the outer independent \([k]\)-Roman domination number \(\gamma_{oi[kR]}(G)\), which we will shorten by OI\([k]\)RD-number. It is worth noting that some studies have already been done on the OI\([k]\)RD-number for \(k=1\) (see for example, [12-14] ) and for \(k=2\) (see for example, [15-17]).
In this paper, we study the outer independent double Roman domination stability (OIDRD-stability) of graphs. The outer independent double Roman domination stability, or just \(\gamma_{oidR}\)–stability, of a graph \(G\) is the minimum size of a set of vertices whose removal changes the outer independent double Roman domination number. We denote the \(\gamma_{oidR}\)-stability of \(G\) by \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\). The \(\gamma_{oidR}^-\)-stability of \(G\), denoted by \({\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\), is defined as the minimum size of a set of vertices whose removal decreases the outer independent double Roman domination number, and the \(\gamma_{oidR}^+\)-stability of \(G\), denoted by \({\rm st}^+_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\), is defined as the minimum size of a set of vertices whose removal increases the outer independent double Roman domination number, if such a set exists. If there is no a set of vertices of \(G\) whose removal increases the outer independent double Roman domination number, then we define \({\rm st}^+_{\gamma_{oidR}}=\infty\). Clearly, \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) = \min\{{\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G), {\rm st}^+_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\}\).
In this paper, we determine the exact values on the \(\gamma_{oidR}\)-stability of some special classes of graphs, and present some bounds on \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\). We also characterize all graphs \(G\) with large \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\). In addition, for a tree \(T\) with maximum degree \(\Delta\), we show that \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T)=1\) and \({\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T)\le \Delta\), and characterize the trees that achieve the upper bound.
In this section, we determine the outer independent double Roman domination stability for some classes of graphs and present various bounds for this parameters. Ahangar et al. [17] observed that:
Proposition 1 ([17]). For \(n\ge1\), \(\gamma_{oidR}(P_{n})=\left\{ \begin{array} [c]{lll}% n & \mathrm{if} & n=3\\ n+1 & & \mathrm{otherwise}. \end{array} \right.\)
Proposition 2 ([17]). For \(n\ge3\), \(\gamma_{oidR}(C_{n})=\left\{ \begin{array} [c]{lll}% n & \mathrm{if} & n\equiv0\pmod{2}\\ n+1 & & \mathrm{otherwise}. \end{array} \right.\)
Next corollaries are immediate consequence of above propositions.
Corollary 1. For \(n\geq 2\), \({\rm st}^{-}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(P_n)=\left\{\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & {\rm if} & n=3\\ 1 & & \mathrm{otherwise}. \end{array}\right.\)
Corollary 2. For \(n\geq 2\), \({\rm st}^{+}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(P_n)=\left\{\begin{array}{ccc} 1 & {\rm if} & n=3\\ \infty & & \mathrm{otherwise}. \end{array}\right.\)
Corollary 3. For \(n\geq 2\), \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(P_n)=1\).
Corollary 4. For \(n\geq 3\), \({\rm st}^{-}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(C_n)=\left\{\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & {\rm if} & n\equiv 0 \pmod{2} \;\mathrm{and}\; n\neq 4 \\ 1 & &\mathrm{otherwise}. \end{array}\right.\)
Corollary 5. For \(n\geq 3\), \({\rm st}^{+}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(C_n)=\infty\).
Corollary 6. For \(n\geq 3\), \[{\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(C_n)=\left\{\begin{array}{ccc} 2 & {\rm if} & n\equiv 0 \pmod{2}\;\mathrm{and}\; n\neq 4\\ 1 & &\mathrm{otherwise}. \end{array}\right.\]
It is observed in [15] that for \(p\geq 1\), \(\gamma_{oidR}(K_p)=p+1\) and for \(p\geq q\geq 1\), \[\gamma_{oidR}(K_{p,q})=\left\{\begin{array}{lll} 3 & {\rm if}& q=1 \\ 2q & {\rm if}& q\in \{2,3\}\\ q+4 & {\rm if}& q\ge 4.\\ \end{array}\right.\]
From the above results, we can easily obtain the following conclusion.
Corollary 7. For \(n\geq 2\), \({\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_n)={\rm st}^+_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_{1, n-1})=1\), \({\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_{1, n-1})=n-1\) and \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_n)={\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_{1, n-1})=1\).
Corollary 8. For \(p\geq q\geq 1\), \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_{p,q})=1\).
In the sequel we present several bounds and characterizations for the OIDRD-stability of a graph. Since for any graph \(G\) of order \(n\ge 2\), \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 3\) with equality if and only if \(G=K_{1,n-1}\), the proof of the first observation is trivial.
Observation 1. If \(G\) is a connected graph of order \(n\ge 2\), then \({\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \le n-1\) with equality if and only if \(G=K_{1,n-1}\).
Proof. The bound follows from the fact that for any graph of order at least two, \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 3\) and that \(\gamma_{oidR}(K_1)=2\).
The sufficiency is clear. Assume now that \({\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) =n-1\). If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\), then for any two adjacent vertices \(u,v\) of \(G\) we have \(\gamma_{oidR}(G[u,v])=3\) and this leads to the contradiction \({\rm st}^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le n-2\). Thus \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)= 3\) and so \(G=K_{1,n-1}\). ◻
Proposition 3. Let \(G\) be a graph of order \(n\ge 2\). Then \[{\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \le \delta(G) + 1.\] This bound is sharp for graphs with isolated vertices.
Proof. Let \(u\) be a vertex of \(G\) with minimum degree \(\delta(G)\), \(G_1 = G-N(u)\) and \(G_2= G- N[u]\). Suppose that \(f\) is a \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\)-function. If \(u\) is an isolated vertex, then \(f(u)=2\) and we have \(\gamma_{oidR}(G_2)=\gamma_{oidR}(G)-2\). Thus \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \le \delta(G) + 1\). So we assume that \(u\) is not an isolated vertex. If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G_1)\neq \gamma_{oidR}(G)\), then \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \le \delta(G) < \delta(G) + 1\). Let \(\gamma_{oidR}(G_1)= \gamma_{oidR}(G)\) and let \(g\) be a \(\gamma_{oidR}(G_1)\)-function. Since \(u\) is an isolated vertex in \(G_1\), \(g(u) = 2\) and we have \(\gamma_{oidR}(G_1)= \gamma_{oidR}(G_2)+2\). That is, \(\gamma_{oidR}(G_2)=\gamma_{oidR}(G)- 2\) and so \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \le \delta(G) + 1\). ◻
Proposition 4. Let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n\) with \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\), then \[{\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G) \le \max\{1,n-\Delta(G)-1\}.\]
Proof. If \(\Delta(G)=2\), then \(G\) is the path \(P_n\) or a cycle \(C_n\) and by Corollary 3 or Corollary 6 we are done. Let \(\Delta(G)\ge 3\) and \(f=(V_0,V_1,V_2,V_3)\) be a \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\)-function. If \(V_1\neq \emptyset\) and \(v\in V_1\), then the restriction of \(f\) on \(G-v\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-v\) with weight \(\omega(f)-1\) and so \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1\). Assume that \(V_1=\emptyset\). Let \(u\) be a vertex with maximum degree \(\Delta(G)\) and \(X=V(G)-N[u]\). We consider some cases based on the value of \(f(u)\).
Case 1. Assume that \(f(u)=3\).
If \(\sum\limits_{x\in X}f(x)>0\), then the restriction of \(f\) on \(G-X\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-X\) with weight less than \(\omega(f)\) and we have \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le st^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le |X|=n-\Delta(G)-1\). Assume that \(\sum\limits_{x\in X}f(x)=0\). If \(X\neq \emptyset\), then there is a vertex \(v\in N(u)\) such that \(f(v)\ge 2\). Then the function \(g\) defined on \(G-X\) by \(g(v)=1\) and \(g(x)=f(x)\) for the remaining vertices, is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-X\) with weight at most \(\omega(f)-1\) and again \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le n-\Delta(G)-1\). Assume that \(X=\emptyset\). Since \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\), there is a vertex \(v\in N(u)\) such that \(f(v)\ge 1\). Then the restriction of \(f\) on \(G-v\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-v\) with weight at most \(\omega(f)-1\) and so \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1\).
Case 2. Assume that \(f(u)=2\).
If \(\sum\limits_{x\in X}f(x)\ge 2\), then the function \(g\) defined on \(G-X\) by \(g(u)=3\) and \(g(x)=f(x)\) for the remaining vertices, is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-X\) with weight at most \(\omega(f)-1\) and so \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le n-\Delta(G)-1\). Assume that \(\sum\limits_{x\in X}f(x)=0\) (note that \(V_1=\emptyset\)). If \(X=\emptyset\), then it follows from \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\) and \(V_1=\emptyset\) that there is a vertex \(v\in N(u)\) such that \(f(v)\ge 2\). Then the function \(g\) defined on \(G-v\) by \(g(u)=3\) and \(g(x)=f(x)\) for the remaining vertices, is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-v\) with weight at most \(\omega(f)-1\) and we have \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1\). Let \(X\neq\emptyset\). Then there is a vertex \(v\in N(u)\) such that \(f(v)=3\) or there are two vertices \(v,w\) in \(N(u)\) such that \(f(v)\ge 2\) and \(f(w)\ge 2\). Define the function \(g\) on \(G-X\) by \(g(u)=3\), \(g(x)=1\) for \(x\in N(u)\cap(V_2\cup V_3)\) and \(g(x)=0\) for the remaining vertices. Clearly \(g\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-X\) with weight at most \(\omega(f)-1\) and so \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le n-\Delta(G)-1\).
Case 3. Assume that \(f(u)=0\).
Since \(f\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G\) with \(V_1=\emptyset\), certainly we have \(f(x)\ge 2\) for each \(x\in N(u)\). Then the function \(g\) defined on \(G-X\) by \(g(u)=2\) and \(g(x)=1\) for the remaining vertices, is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-X\) with weight at most \(\omega(f)-1\) and so \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le n-\Delta(G)-1\). This completes the proof. ◻
In this section we characterize graphs \(G\) with \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\in \{n-1,n-2,n-3,n-4\}\).
Proposition 5. Let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n \ge 2\). Then \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-1\) if and only if \(G = K_2\).
Proof. If \(G = K_2\), then clearly \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1=n-1\). Now we prove the necessity. Let \(G\) be a connected graph with \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-1\). Using Proposition 3 we have \(n-1=st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le \delta(G)+1\), that is \(\delta(G)\ge n-2\). If \(\delta(G)=n-1\), then \(G\) is the complete graph \(K_n\) and Corollary 7 leads to \(G=K_2\), as desired. Assume that \(\delta(G)=n-2\). If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\), then by Proposition 4 we obtain \(n-1=st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le 1\). That is \(n=2\) and so \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)=3\), a contradiction. If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)=3\), then \(G\) is the star \(K_{1,n-1}\) and Corollary 7 leads to \(n-1=st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)= 1\). It follows that \(n=2\) and thus \(G=K_2\). ◻
Proposition 6. Let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n \ge 3\). Then \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-2\) if and only if \(G\in\{ P_3,K_3\}\).
Proof. If \(G\in\{ P_3,K_3\}\), then clearly \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1=n-2\). Now we prove the necessity. Let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n\ge 3\) with \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-2\). Then obviously \(\Delta(G)\ge 2\). If \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1\), then \(n=3\) and we have \(G\in \{P_3,K_3\}\) as desired. Hence we assume that \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\ge 2\). If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\), then Proposition 3 leads to \(\Delta(G)\le 1\) which is a contradiction. So \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)=3\) and \(G\) is the star \(K_{1,n-1}\) which contradicts the fact that \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_{1,n-1})=1\). ◻
Proposition 7. Let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n \ge 4\). Then \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-3\) if and only if \(G\in\{ P_4, C_4, K_4,K_{1,3}+e,K_4-e\}\).
Proof. The sufficiency is straightforward to check. To prove the necessity, let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n \ge 4\) with \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-3\). Obviously \(\Delta(G)\ge 2\). If \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1\), then \(n=4\) and it is easy to verify that \(G\in \{P_4, C_4, K_4,K_{1,3}+e,K_4-e\}\) as desired. Hence we assume that \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\ge 2\) and so \(n\ge 5\). If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)=3\), then \(G\) is the star \(K_{1,n-1}\) and Corollary 7 leads to the contradiction \(1={\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(K_{1,n-1})\ge 2\). Thus \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\). Then Proposition 3 leads to \(\Delta(G)\le 2\), thus \(\Delta(G)= 2\). Combining this with the condition that \(G\) is connected, we have that \(G\) is a path or a cycle. Since \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(P_n)=1\), it follows from \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\ge 2\) that \(G\) is a cycle. Combining Corollary 6 and the condition \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-3\), we obtain that \(n =5\) which is a contradiction. This completes the proof. ◻
Proposition 8. Let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n \ge 6\). Then \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-4\) if and only if \(G\) is the graph illustrated in Figure 1.
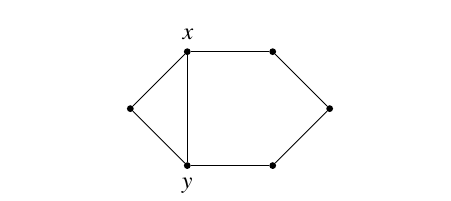
Proof. The sufficiency is straightforward to check. To prove the necessity, let \(G\) be a connected graph of order \(n \ge 6\) with \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=n-4\). Clearly \(\Delta(G)\ge 2\) and \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\ge 2\). So \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 4\). Note that if \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)=3\), then \(G\) is a star \(K_{1,n-1}\) and we have \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=1\) by Corollary 7. It follows from Proposition 3 that \(n-4={\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le \delta+1\) and so \(\delta\ge n-5\). Combining this with Proposition 3, we obtain \[\label{eq1} n-5\le \delta\le \Delta\le 3.\tag{1}\] If \(\Delta(G)=2\), then \(n\in \{6,7\}\) and \(G\) is a path or cycle of order \(n\). It follows from Corollaries 3 and 6 that \(G=C_6\). Henceforth we assume that \(\Delta(G)=3\). By (1) we obtain \(n\in \{6,7,8\}\). Let \(v\in V(G)\) be a vertex with maximum degree 3 with \(N(v)=\{v_1,v_2,v_3\}\) and let \(f=(V_0,V_1,V_2,V_3)\) be a \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\)-function. If \(V_1\neq\emptyset\) and \(z\in V_1\), then the function \(f\) restricted to \(G-z\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-z\) of weight \(\omega(f)-1\) and so \(n-4={\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le 1\) which is a contradiction. Hence we may assume that \(V_1=\emptyset\). Since \(G\) is a connected graph of order \(n\ge 6\) with maximum degree 3, we assume, without loss of generality, that \(u\in N(v_1)-N[v]\). If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 7\), then the function \(g\) defined on \(G[N[v]\cup\{u\}]\) with \(f(v)=f(u)=2\), \(f(v_2)=f(v_3)=1\) and \(f(v_1)=0\) is an OI[2]RDF of weight less that \(\omega(f)\) and so \(n-4={\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le n-\Delta(G)-2\) which leads to the contradiction \(\Delta(G)\le 2\). Thus we may assume that \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\le 6\). We distinguish three cases.
Case 1. Assume that \(n=8\).
By (1) we conclude that \(G\) is a 3-regular graph. So \(G\) has 12 edges. If \(|V_2|+|V_3|\le 3\), then \(V_2\cup V_3\) can cover at most 9 edges of \(G\) and so there are at least three edge between the vertices of \(V_0\), a contradiction with definition. Thus \(|V_2|+|V_3|\ge 4\) and so \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\ge 8\) contradicting the fact \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\le 6\).
Case 2. Assume that \(n=7\).
Since there is no 3-regular graph of order 7, we have \(\delta(G)=2\). By our earlier assumption we have \(2|V_2|+3|V_3|=\gamma_{oidR}(G)\le 6\). This implies \(|V_2|+|V_3|\le 3\), \(|V_2|\le 3\) and \(|V_3|\le 2\). If \(|V_3|=2\) and \(V_3=\{w_1,w_2\}\), then \(|V_0|=5\) and we may assume that three vertices in \(V_0\), say \(z_1,z_2,z_3\) are double Roman dominated by \(w_1\). Then the function \(g\) defined on \(G[\{w_1,w_2,z_1,z_2,z_3\}]\) by \(g(w_1)=3\), \(g(w_2)=2\), \(g(z_1)=g(z_2)=g(z_3)=0\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G[\{w_1,w_2,z_1,z_2,z_3\}]\) of weight less than \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\). So \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le 2<n-4\), a contradiction. If \(|V_3|=1\), then \(|V_2|\le 1\) (since \(2|V_2|+3|V_3|\le 6\)) and all vertices in \(V_0\) must be adjacent to the vertex in \(V_3\) a contradiction with \(\Delta(G)=3\). Thus \(V_3=\emptyset\). If \(|V_2|=2\), then each vertex in \(V_0\) must be adjacent to every vertex in \(V_2\), a contradiction with \(\Delta(G)=3\) again. Henceforth we assume that \(|V_2|=3\). Let \(V_2=\{x_1,x_2,x_3\}\) and \(V_0=\{y_1,y_2,y_3,y_4\}\). Since each vertex in \(V_0\) must be adjacent to at least two vertices in \(V_2\) and since \(\Delta(G)=3\), we may assume that each of \(x_1\) and \(x_2\) is adjacent to three vertices in \(V_0\). Then \(x_1\) and \(x_2\) have certainly two common neighbor in \(V_0\), say \(y_1,y_2\). Let \(x_1y_3\in E(G)\). Then the function \(g\) defined on \(G-\{x_3,y_4\}\) by \(g(x_1)=g(x_2)=2\), \(g(y_3)=1\) and \(g(y_1)=g(y_2)=0\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-\{x_3,y_y\}\) of weight less than \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\). So \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le 2<n-4\), a contradiction.
Case 3. Assume that \(n=6\).
Let \(V(G)=\{v,v_1,v_2,v_3,u,w\}\) where \(N(v)=\{v_1,v_2,v_3\}\) and \(uv_1\in E(G)\). Consider the following situations.
\(f(v)=3\).
Since \(\omega(f)\le 6\), for double Roman dominating the vertices \(u\) and \(w\) either \(f(v_i)=3\) for some \(1\le i\le 3\) or \(f(u)+f(w)=3\). If \(f(v_i)=3\) for some \(1\le i\le 3\), say \(i=1\), then \(f(u)=f(w)=f(v_2)=f(v_3)=0\) and the function \(g\) defined on \(G-v_3\) by \(g(v_2)=2\), \(g(v)=0\), \(g(v_1)=3\) and \(g(u)=g(w)=0\), is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-v_3\) of weight less than \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\). So \(2={\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)\le 1\), which is a contradiction. If \(f(u)+f(w)=3\), then \(f(v_1)=f(v_2)=f(v_3)=0\), and the function \(g\) defined on \(G-w\) by \(g(u)=2\), \(g(v)=3\), \(g(v_1)=g(v_2)=g(v_3)=0\), is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-w\) of weight less than \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\), which leads to a contradiction.
\(f(v)=2\).
Since \(\omega(f)\le 6\), \(n=6\) and \(V_1=\emptyset\), we deduce that \(V_3=\emptyset\) and hence \(|V_2|=3\). Assume that \(V_2=\{x_1,x_2,x_3\}\) and \(V_0=\{y_1,y_2,y_3\}\). If \(x_i\) is adjacent to all vertices in \(V_0\) for some \(i\), say \(i=1\), then the function \(g\) defined on \(G-x_3\) by \(g(x_1)=3\), \(g(x_2)=2\) and \(g(y_1)=g(y_2)=g(y_3)=0\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-x_3\) with weight less than \(\omega(f)\), leading to a contradiction. Thus each \(x_i\) is adjacent to at most two vertices in \(V_0\). On the other hand, since each vertex in \(V_0\) must be adjacent to at least two vertices in \(V_2\), we conclude that each \(x_i\) has exactly two neighbors in \(V_0\). Without loss of generality we may assume that the \(C_6\)-cycle \(C=x_1y_1x_2y_2x_3y_3x_1\) is a subgraph of \(G\). Note that \(V_0\) is independent. Since \(\Delta(G)=3\), we have \(\deg(x_i)=3\) or \(\deg(y_i)=3\) for some \(i\). If \(\deg(y_i)=3\) for some \(i\), then there exists a vertex \(x_j\) which is adjacent to all vertices in \(V_0\), and we have seen above that this is not possible. Hence we assume that \(\deg(y_i)=2\) for each \(i\). This implies \(\deg(x_i)=2\) for some \(i\), say \(i=1\). Then \(G=C+x_2x_3\) and thus \(G\) is the graph illustrated in Figure 1. It is easy to check that \({\rm st}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)=2\) in this case.
\(f(v)=0\).
Since \(f\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G\) with \(\omega(f)\le 6\) with \(V_1=\emptyset\), we certainly have \(f(v_1)=f(v_2)=f(v_3)=2\). Then each of vertices \(u\) and \(w\) is adjacent to at least two vertices in \(\{v_1,v_2,v_3\}\) and so \(u\) and \(w\) have a common neighbor in \(\{v_1,v_2,v_3\}\), say \(v_1\). Then the function \(g\) defined on \(G-v_3\) by \(g(v_1)=3, g(v_2)=2\) and \(g(v)=g(u)=g(w)=0\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(G-v_3\) of weight less than \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\), which leads to a contradiction.
◻
At the end of this section, we present a Nordhaus-Gaddum type inequality for the sum of the outer independent double Roman domination stability of a graph \(G\) and its complement \(\overline{G}\).
Theorem 2. Let \(G\) be a graph of order \(n\ge 2\). Then \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)+st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(\overline{G})\le n\).
Proof. Since \(n\ge 2\), we have \(\min \{\gamma_{oidR}(G),\gamma_{oidR}(\overline{G})\}\ge 3\). If \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)=3\) (the case \(\gamma_{oidR}(\overline{G})=3\) is similar), then \(G\) is the star \(K_{1,n-1}\) and so \(\overline{G}\) has an isolated vertex. Using Corollary 7 and noting that \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(\overline{G})=1\) we obtain \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)+st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(\overline{G})=2\). Now suppose that \(\min \{\gamma_{oidR}(G),\gamma_{oidR}(\overline{G})\}\ge 4\). Since \(\Delta(G)+\Delta(\overline{G})\ge n-1\), we may assume, without loss of generality, that \(\Delta(G)\ge (n-1)/2\). Applying Propositions 3 and 4 we obtain \[\begin{aligned} st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(G)+st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(\overline{G})&\le (n-\Delta(G)-1)+(\delta(\overline{G})+1)\\ &\le (n-\Delta(G)-1)+(n-\Delta(G))\\ &=2n-2\Delta(G)-1\le n. \end{aligned}\] ◻
In this section, we are ready to determine the \(\gamma_{oidR}(T)\)-stability, the \(\gamma_{oidR}^-(T)\)-stability and the \(\gamma_{oidR}^+(T)\)-stability for trees. From Corollary 2, we know that \({\rm st}^+_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T)\) cannot be bounded. The proof of the following observation is straightforward and therefore omitted.
Observation 3.
If \(v\) is a strong support vertex, then there exists a \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\)-function \(f\) that assigns \(3\) to \(v\) and \(0\) to every leaf neighbor of \(v.\)
If \(v\) is a weak support vertex with leaf neighbor \(u,\) then for any \(\gamma_{oidR}(G)\)-function \(f\), \(f(u)+f(v)\geq 2\).
Theorem 4. For every tree \(T\) of order \(n\ge 2\), \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) =1\).
Proof. If \({\rm diam}(T)\le 2\), then \(T\) is a star \(K_{1,n-1}\), and we have \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) =1\) by Corollary 7. If \({\rm diam}(T)=3\), then \(T\) is a double star \(S_{r,s}\) for some \(s\ge r\ge 1\), and one can easily see that \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(S_{r,s}) =1\). If \(\Delta=2\), then \(T=P_n\) and we are done by Proposition 3. Hence we may assume that \({\rm diam}(T)\ge 4\) and \(\Delta\ge 3\). By contradiction, we assume that there exists a tree \(T\) such that \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) \ge 2\). We choose such a tree with smallest order. First let \(T\) has a strong support vertex \(v\) with leaf neighbors \(v_1,\dots,v_t\). Then the vertices \(v_1,\dots,v_t\) are isolated vertices in \(T'=T-v\) and any \(\gamma_{oidR}(T')\)-function certainly assigns 2 to each \(v_i\). Now reassigning \(v_1,\dots,v_t\) the value 0 and \(v\) the value 3 provides an OI[2]RDF of \(T\) of weight less than \(\gamma_{oidR}(T')\) and this leads to a contradiction. Henceforth, we may assume that \(T\) has no strong support vertex. Let \(p=x_1 x_2 \dots x_t\) be a longest path in \(T\) and root the tree \(T\) at the vertex \(x_t\). Let \(f=(V_0,V_1,V_2,V_3)\) be a \(\gamma_{oidR}(T)\)-function such that \(f(x_3)\) is maximized. It follows from \(st_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) \ge 2\) that \(V_1=\emptyset\). Since \(T\) has no strong support vertex, each child of \(v_3\) with depth 1 has degree 2. We consider the cases.
Case 1. \(x_3\) has a child \(w\) with depth 0, that is \(w\) is a leaf neighbor of \(x_3\).
It is easy to verify that \(f(x_1)+f(x_2)+f(x_3)+f(w)\ge 5\) and by the choice of \(f\) certainly we have \(f(x_3)=3\), \(f(x_1)=2\) and \(f(w)=f(x_2)=0\). This implies that \(\gamma_{oidR}(T-x_1)<\gamma_{oidR}(T)\) which leads to a contradiction.
Case 2. \(x_3\) has a child \(u_2\neq x_2\) with depth 1.
Let \(u_1\) be the leaf neighbor of \(u_2\). It is easy to verify that \(f(x_1)+f(x_2)+f(x_3)+f(u_2)+f(u_1)\ge 6\) and by the choice of \(f\) certainly we have \(f(x_3)\ge 2\), \(f(x_1)=f(u_1)=2\) and \(f(u_2)=f(x_2)=0\). Then the function \(g\) defined on \(T-x_1\) by \(g(x_3)=3\), \(g(v)=f(v)\) for each vertex \(v\in V(T-x_1)-\{x_3\}\), is an OI[2]RDF of \(T-x_1\) of weight at most \(\omega(f)-1\) and so \(\gamma_{oidR}(T-x_1)<\gamma_{oidR}(T)\) leading to a contradiction.
Case 3. \(\deg(x_3)=2\).
By Observation 3 we have \(f(x_1)+f(x_2)\ge 2\). If \(f(x_1)+f(x_2)=2\), then we must have \(f(x_1)=2\), \(f(x_2)=0\) and \(f(x_3)\ge 2\). Then reassigning \(x_3\) the value 3 provides an OI[2]RDF of \(T-x_1\) of weight less than \(\omega(f)\) which leads to a contradiction. Assume that \(f(x_1)+f(x_2)=3\). If \(f(x_2)\le 2\), then reassigning \(x_2\) the value 2 provides an OI[2]RDF of \(T-x_1\) which leads to a contradiction. Hence we may assume that \(f(x_2)=3\) and \(f(x_1)=0\). If \(f(x_3)=0\), then since \(f\) is an OIDRDF with \(V_1=\emptyset\), we have \(f(x_4)\ge 2\) and reassigning \(x_2\) the value 2 provides an OI[2]RDF of \(T-x_1\) which leads to a contradiction. If also \(f(x_3)\ge 2\), then reassigning \(x_2\) the value 1 provides an OI[2]RDF of \(T-x_1\) which leads to a contradiction again. This completes the proof. ◻
Finally, we will establish an upper bound on the \(\gamma_{oidR}^-\)-stability of a tree. Moreover, we characterize the trees that achieve the upper bound.
Theorem 5 . For every tree \(T\) of order \(n\ge 2\) with maximum degree \(\Delta\), \(st^{-}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) \le \Delta\) with equality if and only if \(T\) is the star \(K_{1,n-1}\).
Proof. If \(\Delta=2\), then \(T=P_n\) and we are done by Corollary 7. If \({\rm diam}(T)\le 2\), then \(T\) is a star \(K_{1,n-1}\), and we have \(st^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) =n-1= \Delta\), by Corollary 7. Hence we may assume that \(\Delta\ge 3\) and \({\rm diam}(T)\ge 3\). Let \(p=x_1 x_2 \dots x_t\) be a longest path in \(T\) and root the tree \(T\) at the vertex \(x_t\). Let \(f\) be a \(\gamma_{oidR}(T)\)-function such that \(f(x_3)\) is maximized. Assume first that \(\deg(x_2) < \Delta\). We have clearly \(f(x_1)+f(x_2)\ge 2\) and \(f(x_1)+f(x_2)+f(x_3)\ge 3\). Let \(T^\prime\) be the tree obtained from \(T\) by removing all vertices of \(T_{x_2}\). Define the function \(f^{\prime} : V (T^\prime) \to \{0, 1, 2, 3\}\) by \(f^\prime (x_3) = \max\{2, f(x_3)\}\) and \(f^\prime(y) = f(y)\) for each \(y \in V (T^\prime) \setminus \{x_3\}\). It is not hard to see that \(f^\prime\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(T^\prime\). Since \(\gamma_{oidR}(T^\prime) \le w(f^\prime) \le w(f)-1 = \gamma_{oidR}(T) -1\), we have \(st^{-}_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) < \Delta\). Hence we may assume that \(\deg(x_2) =\Delta\). Similarly, we may assume that every child of \(x_3\) with depth 1, is of degree \(\Delta\). By Observation 3, \(f\) assign 3 to each child of \(x_3\) with depth 1, in particular to \(x_2\). If \(f(x_3)\neq 0\), then remove all leaves adjacent to \(x_2\), and denote the resulting graph by \(T^\prime\). Define the function \(f^\prime : V (T^\prime) \to \{0, 1, 2, 3\}\) by \(f^\prime(x_2) = 0, f^\prime(x_3)= 3\) and \(f^\prime(y) = f(y)\) for any \(y \in V (T^\prime) \setminus \{x_2, x_3\}\). Clearly, \(f^\prime\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(T^\prime\) with weight at most \(\gamma_{oidR}(T) -1\), so we have \(st^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) < \Delta\). Henceforth, we may assume that \(f(x_3)=0\). Since \(f\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(T\), we must have \(f(x_4)\ge 1\). If \(f(x_4)=1\), then the restriction of \(f\) to \(T-x_4\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(T-x_4\) with weight \(\gamma_{oidR}(T) -1\), so we have \(st^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) =1< \Delta\). Assume that \(f(x_4)\ge 2\). Remove all leaf-neighbors of \(x_2\), and denote the resulting graph by \(T^\prime\). Define the function \(g : V (T^\prime)\to\{0, 1, 2, 3\}\) by \(g(x_2) = 2\) and \(g(x) = f(x)\) for any \(x\in V (T^\prime) \setminus \{x_2\}\). It is easy to see that \(g\) is an OI[2]RDF of \(T^\prime\) with weight \(\gamma_{oidR}(T) -1\), so we have \(st^-_{\gamma_{oidR}}(T) < \Delta\). This completes the proof. ◻
The authors declare no conflicts of interest to this work.